Ischemic refers to a medical condition or event that is caused by inadequate blood
supply to a specific area of the body, typically due to a
blockage in the arteries. This lack of blood flow can lead to tissue damage and potentially life-threatening complications.
Causes:
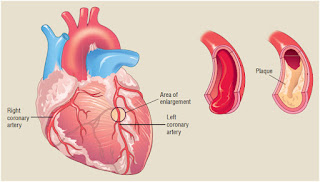
1. Atherosclerosis: The most common cause of ischemia is the narrowing or hardening of
arteries due to the
buildup of fatty plaques, a condition known as atherosclerosis.
2. Blood clots: Blood clots can form within blood vessels and
restrict blood flow, resulting in ischemia.
3. Embolism: An embolism occurs when a blood clot or other debris travels through the bloodstream and blocks a smaller artery.
Signs and Symptoms:
1. Chest pain or angina: A common symptom of ischemia affecting the heart is chest pain or discomfort, which may radiate to the arms, neck, jaw, or back.
2. Shortness of breath: Ischemia can cause difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
3. Fatigue: Reduced blood flow can lead to a general feeling of weakness or excessive tiredness.
4. Numbness or weakness: If ischemia affects the brain, it may cause numbness or weakness in one side of the body, difficulty speaking, or confusion.
5. Pain or cramping: Ischemia in the legs can cause pain, cramping, or heaviness during physical activity.
Prevention Measures:
1. Quit smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and accelerates the development of atherosclerosis. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of ischemic events.
2. Healthy diet: Adopting a diet low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium, and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is beneficial for heart health.
3. Regular exercise: Engaging in moderate-intensity aerobic exercises, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, at least 150 minutes per week, can improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of ischemia.
4. Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight increases the risk of developing conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, all of which contribute to ischemic events.
5. Manage chronic conditions: Control conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular medical check-ups.
6. Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Moderation is key.
7. Medication: In some cases, medication such as aspirin, anticoagulants, or cholesterol-lowering drugs may be prescribed to manage the underlying causes of ischemia.
Please note that this information is for educational purposes only, and consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies.
.jpeg)






.jpeg)



.jpeg)




